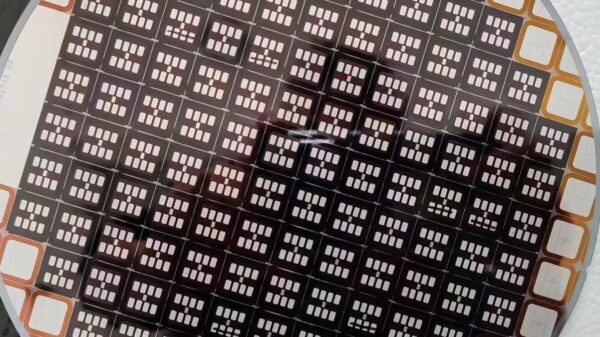
In the rapidly evolving field of power electronics, wide bandgap (WBG) semiconductors such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) are gaining prominence. These materials, known for their superior energy efficiency, are projected to capture a significant market share in the power semiconductor sector, potentially reaching 45% by 2035.
The interest in WBG semiconductors was evident at the "Japan-Germany October Technology Exchange Meeting" hosted by the German Chamber of Commerce and Industry in Japan in October 2023. During this event, Professor Hiroshi Amano of Nagoya University, a Nobel laureate recognized for his development of blue LEDs, discussed the. . .